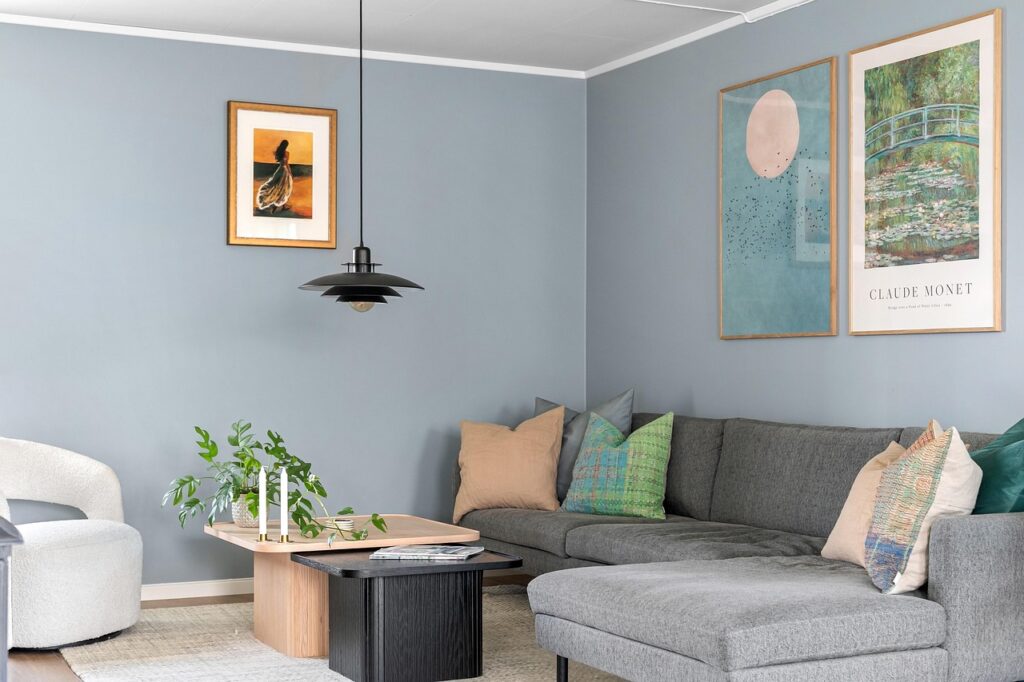
Urban housing in Nigeria has evolved significantly over the past few decades, yet few developments have stood the test of time and planning excellence like Shagari Estate. Conceived as a visionary response to housing shortages and rapid urbanization, this estate reflects a balance between functionality, community, and affordability.
Built during a transformative era in Nigeria’s urban development, the estate represents a legacy of social housing initiatives that aimed to provide quality homes for citizens from all walks of life. Today, it remains a relevant example of how well-designed communities can positively influence the way people live, interact, and grow.
This article explores the history, structure, features, and future of this remarkable housing project shedding light on what makes it one of Nigeria’s most respected residential landmarks.
The Origins and Vision Behind Shagari Estate
The development of Shagari Estate dates back to the early 1980s, during the administration of President Shehu Shagari. At that time, Nigeria was facing an increasing demand for affordable and well-planned residential spaces. The government launched a nationwide housing initiative to reduce the growing urban housing deficit and promote homeownership among middle and lower-income citizens.
The estate was designed not only to provide shelter but also to establish sustainable communities with basic amenities such as schools, healthcare centers, and marketplaces. Each unit was built to reflect practical living conditions for families, emphasizing simplicity, ventilation, and durability key priorities in tropical architecture.
This government-led housing program symbolized hope, progress, and national development. Decades later, the estate still stands as a testament to Nigeria’s early attempts at structured housing policy and community planning.
Architectural Design and Urban Planning
Layout and Structure
The architectural layout of Shagari Estate was guided by principles of order, accessibility, and communal living. Streets were organized into grids and cul-de-sacs to limit traffic congestion while fostering a neighborhood feel. Housing units were strategically positioned to maximize space and natural light, ensuring both privacy and connectivity among residents.
The estate consists of a mix of bungalows, duplexes, and low-rise apartment blocks. This diversity allowed people from various income brackets to find suitable accommodations within the same development. The houses were typically built with locally sourced materials, cement blocks, roofing sheets, and reinforced concrete to promote sustainability and reduce construction costs.
Green Spaces and Environment
Urban planners integrated green belts and communal gardens within the estate, promoting outdoor recreation and environmental well-being. These open areas not only serve aesthetic purposes but also help regulate temperature, manage drainage, and provide residents with relaxing spaces for social interaction.
This approach aligns with modern sustainability principles that advocate for balanced coexistence between infrastructure and nature.
Social Infrastructure and Community Development
A crucial factor behind the estate’s enduring success is its comprehensive social infrastructure. Unlike many modern private estates that focus primarily on luxury, Shagari Estate prioritized livability and accessibility.
Key facilities within the community typically include:
- Educational institutions: Primary and secondary schools to support families living in the estate.
- Healthcare centers: Clinics and pharmacies providing essential medical services within walking distance.
- Markets and shopping centers: Designed for everyday convenience and economic activity.
- Religious centers: Mosques and churches catering to residents’ spiritual and social needs.
- Playgrounds and recreational zones: Spaces for children, youth, and families to interact safely.
These facilities help create a sense of belonging and community cohesion. Over time, many residents have developed strong social networks that continue to define the estate’s unique culture and identity.
Shagari Estate in Major Nigerian Cities
Lagos
The most prominent version of the estate can be found in Lagos, specifically in areas such as Ipaja and Iyana Ipaja. This development forms part of the larger Lagos State housing ecosystem, surrounded by major roads and accessible via public transport. The location allows residents to enjoy proximity to central business districts while still benefiting from a quieter suburban atmosphere.
Over the years, the Lagos site has undergone gradual modernization. Private renovations, upgraded facilities, and better road networks have improved its overall appeal. Despite urban pressures, the estate continues to serve as a residential haven for thousands of families.
Abuja and Other Locations
Apart from Lagos, variations of the estate model can also be found in other states such as Abuja, Kaduna, and Port Harcourt. Each development retains the core design philosophy affordability, structure, and functionality while adapting to local urban needs.
These estates collectively represent a national model of public housing that influenced later residential developments across Nigeria.
Economic and Real Estate Value
Housing Affordability and Ownership
When originally constructed, the homes were sold or allocated at subsidized rates to make them affordable for average income earners. This approach contributed to increasing the number of homeowners in urban areas a major achievement in Nigeria’s housing history.
Even today, the estate remains an attractive choice for both homeowners and tenants seeking stability and value for money. The properties, though older, maintain strong demand because of their central locations, solid construction, and established infrastructure.
Property Appreciation and Investment
Real estate experts note that properties within the estate have appreciated significantly over the past two decades. Investors who purchased units early on have seen consistent returns, as urban expansion and improved transport links continue to boost property values.
This steady growth highlights the estate’s resilience in a market often characterized by volatility. For new investors, refurbished units and modernized extensions now offer lucrative rental opportunities — particularly for young professionals and families looking for secure environments with accessible amenities.
Challenges and Modernization Efforts
While the estate remains a success story, it also faces several challenges common to aging public housing projects. These include infrastructure decay, inadequate maintenance, and limited modernization. Roads, drainage systems, and waste management facilities in some sections have deteriorated over time.
However, ongoing government and community-led initiatives aim to revitalize the estate. Renovation projects include road resurfacing, installation of solar street lights, and redevelopment of public facilities. In addition, many private homeowners have upgraded their properties, blending traditional designs with modern architecture.
Public-private partnerships have also been proposed to ensure sustainable funding for infrastructure upgrades, highlighting a growing recognition of the estate’s value as a historical and functional asset.
Cultural Significance and Community Life
Beyond its architectural and economic contributions, the estate has developed a rich social culture. Residents often describe their community as close-knit and family-oriented, with shared traditions and events that strengthen unity.
Festivals, neighborhood meetings, and religious gatherings provide opportunities for interaction and mutual support. Children grow up in secure environments where neighbors know and trust each other an increasingly rare dynamic in today’s fast-paced urban centers.
This sense of belonging underscores one of the estate’s greatest strengths: it fosters not just housing, but genuine community living.
Urban Impact and Lessons for Future Housing Projects
Urban planners and policymakers continue to study Shagari Estate as a reference point for effective housing policy in developing economies. It demonstrates that affordability, sustainability, and livability can coexist when proper planning and government commitment align.
Future housing projects can draw several lessons from this model:
- Integrated Planning: Housing must include education, healthcare, and commerce within walkable distances.
- Community Participation: Engaging residents in management improves maintenance and social harmony.
- Sustainability: Local materials, energy-efficient design, and green spaces are essential.
- Affordability: Government-led schemes should balance cost recovery with social welfare.
- Adaptability: Housing designs should evolve to meet changing population needs and modern lifestyles.
These insights are vital for Nigeria’s continuing effort to close its housing gap and ensure equitable access to quality urban living.
Government Policy and the Future of Public Housing
Public housing policy in Nigeria has shifted over the years from direct government construction to public-private collaborations. However, the foundational vision behind projects like Shagari Estate remains relevant: the belief that every citizen deserves a safe, decent, and affordable home.
As cities expand and demand for housing rises, policymakers are revisiting older estate models to modernize them for current realities. By integrating digital infrastructure, green technology, and improved financing systems, the goal is to replicate the community-oriented success of past developments while adapting to modern expectations.
The future of Nigerian housing may depend on how effectively these traditional estates are rejuvenated and expanded upon blending heritage with innovation.
Conclusion
Shagari Estate stands as more than just a cluster of houses; it is a symbol of vision, governance, and community development. Its enduring presence across Nigeria reflects the long-term value of structured urban planning and affordable housing policies.
The estate’s ability to adapt to changing times while maintaining its cultural and social essence makes it a model worth emulating. For residents, it represents stability and pride; for policymakers, it offers a blueprint for future housing strategies.
As Nigeria continues to evolve, revitalizing and preserving such communities will be essential in ensuring inclusive, sustainable, and dignified living for generations to come.
Call-to-Action:
For investors, planners, or citizens seeking to understand how planned communities shape better lives, exploring developments inspired by this estate provides valuable insights into Nigeria’s path toward sustainable urban growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the historical background of Shagari Estate?
It was established in the early 1980s as part of Nigeria’s public housing program initiated during President Shehu Shagari’s administration, aimed at providing affordable homes.
2. Where is Shagari Estate located?
It has several locations across Nigeria, with the most well-known being in Lagos (Ipaja area). Other versions exist in cities such as Abuja, Kaduna, and Port Harcourt.
3. What type of houses are found in Shagari Estate?
The estate includes a mix of bungalows, duplexes, and low-rise flats, designed to cater to different family sizes and income levels.
4. What amenities are available in Shagari Estate?
Residents enjoy access to schools, clinics, markets, places of worship, playgrounds, and green spaces creating a well-balanced community.
5. Is Shagari Estate still a good investment today?
Yes. Despite being an older development, it remains in high demand due to its strategic locations, durable construction, and established community life.
6. How is Shagari Estate being maintained today?
Both government bodies and residents’ associations are involved in ongoing maintenance and modernization projects, including road rehabilitation and improved waste management.
7. What makes Shagari Estate unique among Nigerian housing estates?
Its combination of affordability, planned infrastructure, and strong community spirit sets it apart as one of the most successful public housing models in the country.